Restore to Azure Virtual Machine
This wizard page enables you to restore a disk image to a Microsoft Azure virtual machine.
In case your backup data selected for restore contains UEFI partitions, refer to the UEFI Partition Restore for Cloud VMs chapter
Before running this wizard, you need to create a new user and select a subscription, region, resource groups, as well as create a storage account and virtual network via the Microsoft Azure Portal.
To be able to restore a disk image, you should use a general-purpose storage account and not a blob storage, because blob storage accounts support only block and append blobs, and not page blobs on on which virtual machines are stored. Page blobs are only available in general-purpose accounts and they do not provide zone-redundant storage (ZRS).
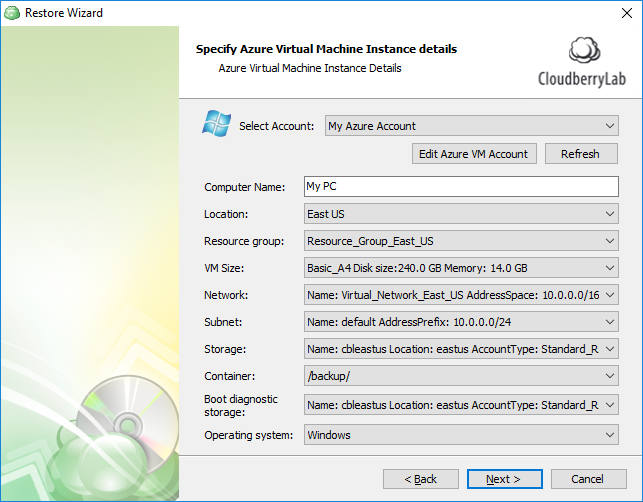
Next, you need to select an existing Azure account or create and configure a new one on this wizard page.
After you selected an account, specify the following options:
Computer name Specifies the name of the created virtual machine
Location Specifies the VM location.
Please be informed that transferring data between different locations takes more time than performing data transfer within a single location.
Resource group Specifies the container that holds related resources (such as virtual machines, storage accounts, web apps, databases, and virtual networks) for an Azure solution. See Resource groups for more information.
VM size
Specifies the size of the target virtual machine.The "Disk size" value displayed for a virtual machine selected on this wizard page indicates a space allocated by Microsoft Azure for storing various temporary information (such as swap files and memory page data). This value is not related to the total size that a restored disk can have (which is limited to 2 TB for Azure virtual machines). See the following documents for more information:
Network
When you create an Azure virtual machine, you must create a new virtual network (VNet) or use an existing one.The specifies network must belong to the same location and resource group as the specified storage (see below). Otherwise, you will not be able to set up a virtual machine. See the following Knowledge Base article for more information: Cannot specify all Azure Virtual Machine instance details in the restore wizard.
Subnet
Specifies the subnet in the virtual network.A subnet is a range of IP addresses in the VNet. You can divide a VNet into multiple subnets for organization and security. Each NIC in a VM is connected to one subnet in one VNet. NICs connected to subnets (same or different) within a VNet can communicate with each other without any extra configuration.
See the following document for more information: Virtual networks and virtual machines in Azure.
Storage
Specifies the disk storage on the target virtual machine.The specified storage must belong to the same location and resource group as the specified network (see above). Otherwise, you will not be able to set up a virtual machine. See the following Knowledge Base article for more information: Cannot specify all Azure Virtual Machine instance details in the restore wizard.
Container Specifies the bucket to which the virtual machine's disks will be placed.
Boot diagnostic storage
Specifies the storage for boot diagnostic files.We strongly recommend that you never disable boot diagnostics when restoring a disk image on an Azure machine. Otherwise, you will not be able to find out the reason of why the restore process has failed. This is because an Azure virtual machine can only be accessed via the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and unlike a VMware workstation, you cannot access an Azure virtual machine unless it has an operating system, network, RDP service and external IP address assigned to it.
Boot diagnostics provides a machine's screenshot that may become critical for accessing the restored machine. Please keep in mind that Azure launches a virtual machine silently, without any warnings, and you will be charged regardless of whether or not its operating system has been launched and of whether or not you are able to access the restored machine.
You need to use a regular storage account for storing boot diagnostics. The premium account is only used to store page blobs (and virtual machine disks) and comes at a much higher price as it uses SSD. See Azure Managed Disks Overview for more information.
Azure Virtual Machine Agent is not automatically installed during VM import. You can manually install it if required. See the following documents for more information:
Operating system
Specifies the operating system of the target virtual machine.If you are restoring a Windows virtual machine, we recommend that you do not select Linux.
When restoring a backup from Amazon S3, the wizard prompts you whether to use a temporary instance on the next wizard page. See Specify the Temporary Instance for more information.