Synthetic Full Backup
This article applies to the new backup format only. For the information about synthetic full backup in the legacy backup format refer to another article
A synthetic full backup is a type of backup that creates a full backup using in-cloud data copying, significantly improving speed and efficiency by saving time and reducing network traffic. This method combines synthetic incremental backups with in-cloud data copying, where data is copied on the cloud side only, making it much faster than traditional full backups from an endpoint to cloud.
How It Works
A synthetic backup is completed in three stages:
- Incremental Backup.
- This stage creates a new restore point in the current backup generation. After a successful synthetic incremental backup, all necessary data for the synthetic full backup is stored in the backup storage.
- In-Cloud Data Copying.
- After the synthetic incremental backup is completed, a new backup generation is created. Data from the previous generation is copied to this new generation, along with the data uploaded during the synthetic incremental backup within the cloud storage.
- Note: Not all storage providers support in-cloud copying. Refer to the Support for Major Storage Providers section
- Deletion of Synthetic Incremental Data.
- Once the data copying within the cloud is successfully completed, the synthetic incremental backup data from the previous generation is deleted, marking the synthetic backup as complete and successful.
Questions and Answers
Q: What happens if a synthetic full backup is interrupted for some reason?
A: The result depends on the stage of interruption. If the synthetic incremental backup was successful but the in-cloud copying was interrupted (e.g., due to network issues), the new generation will be deleted, and the successful synthetic incremental backup will remain valid for the previous generation. If the synthetic incremental backup fails, it is treated as a regular backup failure.
Synthetic Backup Applicability
Synthetic backup applies for the following backup types:
Support for Major Storage Providers
Synthetic full backups are supported by the following storage providers::
- Amazon S3 (except S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval and S3 Glacier Deep Archive storage classes)
- Microsoft Azure (except Azure Archive)
- Backblaze B2
- Wasabi
- MinIO (should be allowed manually)
- S3-compatible storage (depends on the provider and should be allowed manually)
The minimum data part size limitations for in-cloud copying imposed by storage providers may result in the presence of some metadata in the storage
Synthetic Full Backup for MinIO and Other S3-Compatible Storage Accounts
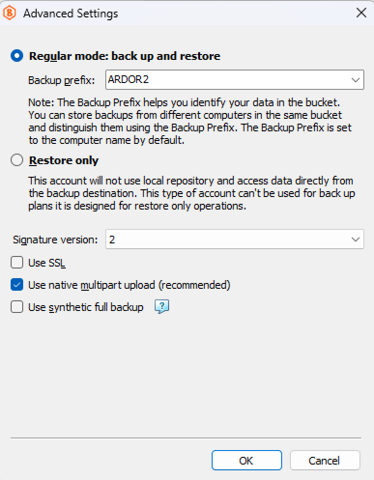
For MinIO and other S3-compatible storage accounts, synthetic full backup is enabled in the storage account properties. To allow usage of the synthetic full backup, proceed as follows:
- In the application menu, select Edit Storage Accounts.
- Find the required storage account then click Edit.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- Select the Use synthetic full backup check box.
- Click OK.
You can now enable or disable synthetic full backup within the backup plans associated with these storage accounts.
Synthetic Full Backup in Backup Plans
Starting from MSP360 (formerly CloudBerry) Backup version 8.0, you can enable or disable synthetic full backups within backup plans where the storage accounts support this feature.
Enable/Disable Synthetic Full Backup
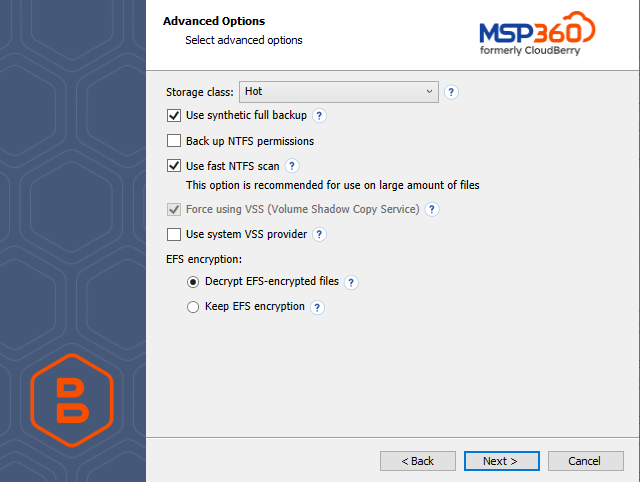
To manage the synthetic full backup for a specific backup plan, proceed as follows:
- On the Backup Plans tab, select the plan you wish to manage and expand it.
- Click Edit and proceed to the Advanced Settings step.
- Select the Use synthetic full backup checkbox to enable the synthetic full backup, or clear the checkbox to disable.
- Proceed with the backup plan and click Finish.
Every time you edit a backup plan, the synthetic full backup conditions are re-evaluated. The synthetic full backup may be disabled if the changes you made affect compatibility (for instance, if you updated the storage account to a destination that doesn’t support synthetic full backups)
Force Synthetic Full Backup
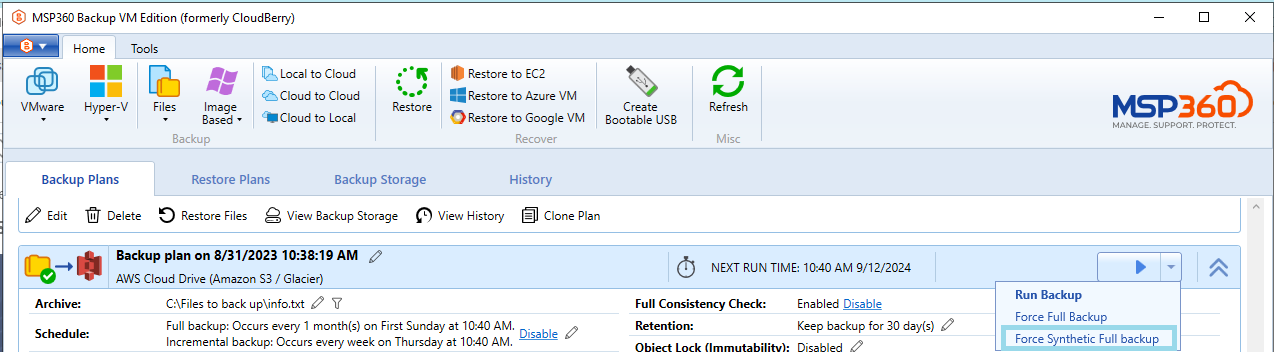
If you want to force a synthetic backup for a backup plan:
- Select the backup plan for which you want to force a synthetic full backup and expand it..
- On the Run control, open the drop-down menu.
- Click Force Synthetic Full Backup.
If you change the compression and/or encryption settings, a synthetic full backup will not be forced. A full backup will be required instead