Step 6. Advanced Options
On this wizard step, configure advanced options for your backup plan.
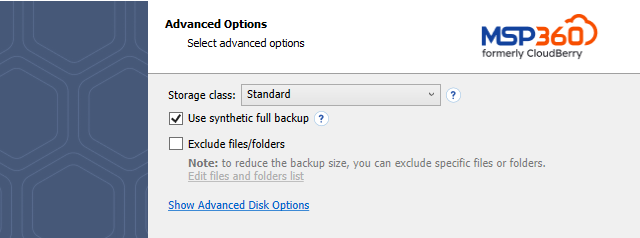
The following settings are available on this wizard page:
Use synthetic full backup. A synthetic full backup is a combination of a full and incremental (block-level) backups. As opposed to a full backup, a synthetic full backup does not upload a full version to the target storage with each backup. Instead, it assembles a new revision directly in the target storage by combining already existing blocks from previous revisions with newly uploaded blocks. This enables you to upload less data to the target storage and speed up the upload process. With this option enabled, the first run of your backup plan will automatically force a full backup (synthetic backups will be executed during subsequent runs of this backup plan).
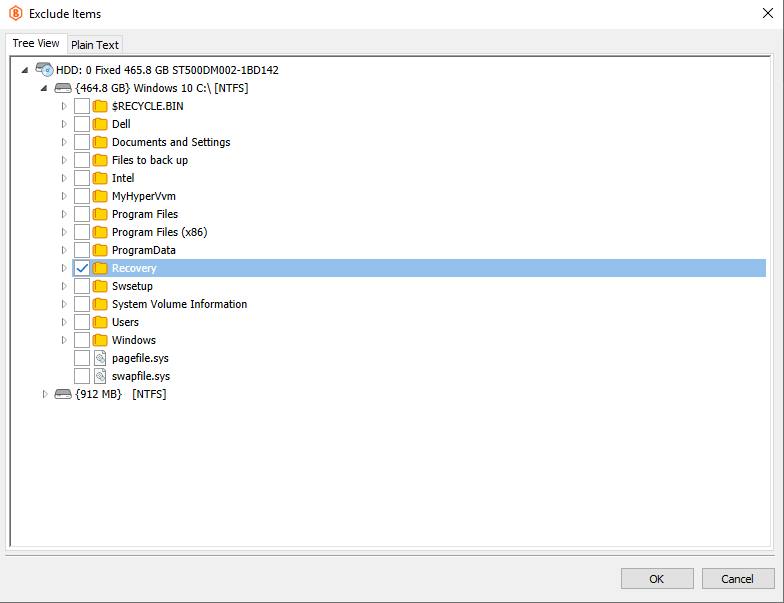
Exclude files/folders. Select this check box to specify files and folders on selected drives to be excluded from your backup. List excluded files/folders using a visual editor that is invoked by clicking the Edit files and folders list link.
Advanced Disk Options
You can customize the additional options. To open this settings group, click Show Advanced Disk Options.
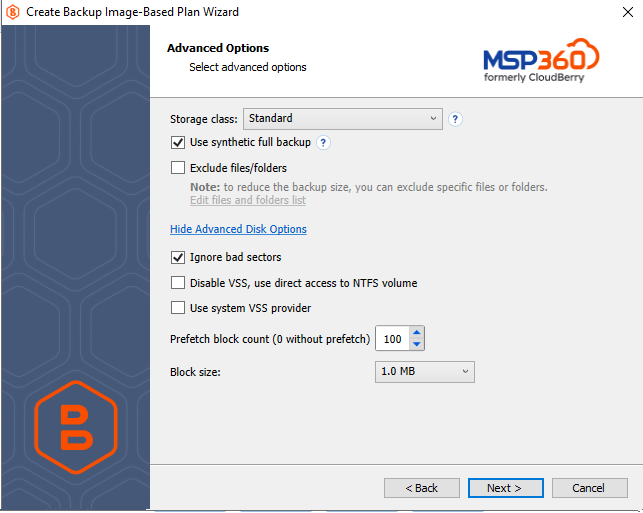
Ignore bad sectors. Enable this option to allow the recovery process to complete after encountering any damaged sectors on a local storage drive. After restoring such a volume, bad sectors will become empty sectors and you will not be able to read any files that were allocated in bad sectors.
Disable VSS, use direct access to NTFS volume. Disables Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS), which may be required when a disk is not used for writing operations and has not enough space to create a VSS snapshot (typically, this is the case with system volumes).
Use system VSS provider. This option forces MSP360 (CloudBerry) Backup to use the system default VSS provider. Select this check box in case of presence of any third-party VSS providers installed on the system that may interfere with proper processing of VSS snapshots by MSP360 (CloudBerry) Backup.
Prefetch block count. Specifies the maximum number of blocks that MSP360 (CloudBerry) Backup can store in memory for each disk volume.
A block is a minimum unit of information that MSP360 (CloudBerry) Backup can process at a time when preparing a backup.
When you need to perform a block-level backup over a disk containing several terabytes of data, you can speed up the backup processing by increasing the block size.
Block size. Specifies the amount of data MSP360 (CloudBerry) Backup can process at a time. Recommended size is 1 MB.
Additional Advanced Options for Amazon S3
If your backup storage destination is Amazon S3, select the S3 storage class for the backup plan:
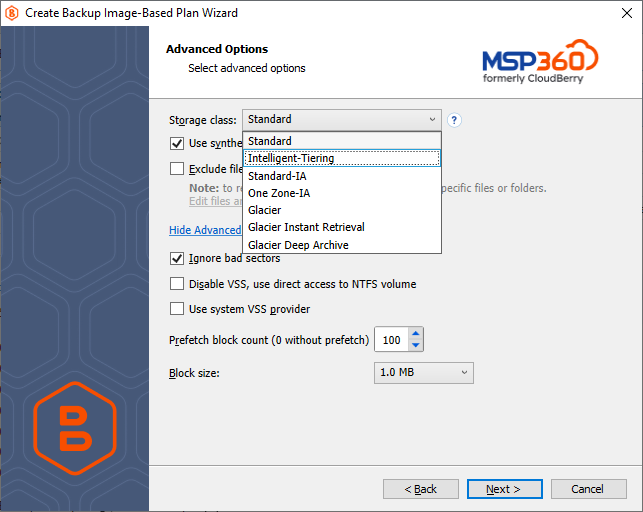
- Standard
- Intelligent-Tiering
- Standard-IA
- One Zone-IA
- Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Glacier Flexible Retrieval (formerly S3 Glacier)
- Glacier Deep Archive
Usage of different storage classes for different backups is the subject of optimizing your storage costs.
Learn more about Amazon S3 storage classes here
Additional Advanced Options for Microsoft Azure
If your backup storage destination is Microsoft Azure, and you have the General Purpose v2 Azure account, select the required storage class (access tier).
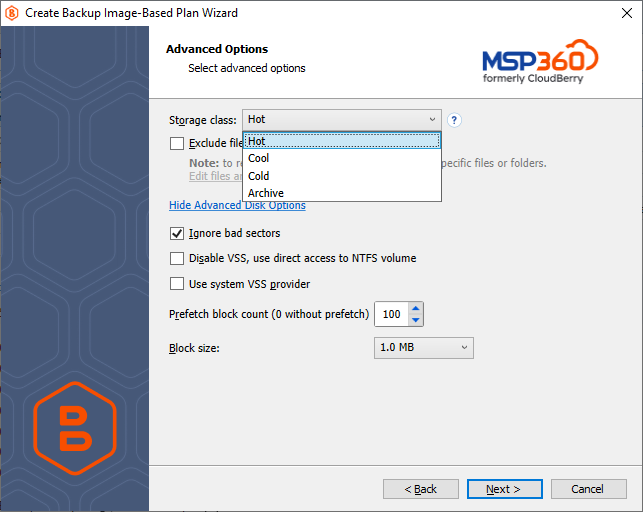
The following options are available:
- Hot tier. An online tier optimized for storing data that is accessed or modified frequently. The hot tier has the highest storage costs, but the lowest access costs.
- Cool tier. An online tier optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed or modified. Data in the cool tier should be stored for a minimum of 30 days. The cool tier has lower storage costs and higher access costs compared to the hot tier.
- Cold tier. An online tier optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed or modified, but still requires fast retrieval. Data in the cold tier should be stored for a minimum of 90 days. The cold tier has lower storage costs and higher access costs compared to the cool tier.
- Archive tier. An offline tier optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed, and that has flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours. Data in the archive tier should be stored for a minimum of 180 days.
Note that this feature is only supported for General Purpose v2 Azure accounts. If you are using another kind of account, you need to upgrade your account to be able to use this feature
Be aware of the additional charges and increased blob access rates after your Azure account upgrade
To learn more about the difference between Azure storage tiers, refer to the Azure Blob Storage - Hot, cool,cold, and archive storage tiers article at docs.microsoft.com.