Restore Verification for Image-Based Backups
Restore Verification is a special feature that checks backup for a further guaranteed restore. Restore Verification is available for image-based backups and can be executed locally (on your computer) and in virtual environments (when Backup for Windows is installed on VMware or Hyper-V virtual machines).
This chapter covers the following topics:
- How It Works
- System Requirements
- Run Restore Verification
- Enable Restore Verification in Backup Plan
- Restore Verification in Long-Term Storage
How It Works
Restore verification is an auxiliary restore plan that retrieves only necessary backup parts from backup storage, mounts a Hyper-V virtual machine on the fly, then performs a system logon.
Since there is no need to download the whole backup dataset to make sure the image-based backup is fully valid and can be guaranteed to restore, the restore verification is performed quickly and clearly. The amount of data on partitions not related to system boot does not affect restore verification time.
For example, when backing up a system disk of 160 GB size and with 120 GB of occupied disk space, restore verification downloads only 8 GB from backup storage and takes a few seconds from the start to a system logon
Restore verification is supported by Windows 8 (Pro and Enterprise editions) and later versions, and Windows Server 2012 R2 and later versions.
System Requirements
Since the restore verification feature is based on Hyper-V mechanisms, a Hyper-V environment is required on your operating system.
The table below contains the list of supported Windows versions and editions.
| Windows Version | Supported Editions |
|---|---|
| Windows 8 | Enterprise, Pro |
| Windows 8.1 | Enterprise, Pro |
| Windows 10 | Enterprise, Pro, Education |
| Windows 11 | Pro |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Essentials, Enterprise, Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2016 | Standard, Essentials, Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2019 | Standard, Essentials, Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2022 | Standard, Datacenter |
As of Backup for Windows version 7.5, the environment required for Restore Verification is installed automatically. In case the installation fails, you will be informed with the appropriate warning (code 2042). Generally, a simple computer reboot helps. In case the installation failure persists, try to perofrm the installation via the command line.
Use the following command: cloudberry backup.exe /installdiskdriver
Run Restore Verification
To run a restore verification for image-based backup, perform the following steps:
- Switch to the Backup Storage tab.
- Find a required image-based backup plan generation.
- Expand the generation to select a required restore point.
- Right-click on the required Restore Point, then select Restore Verification (BETA)
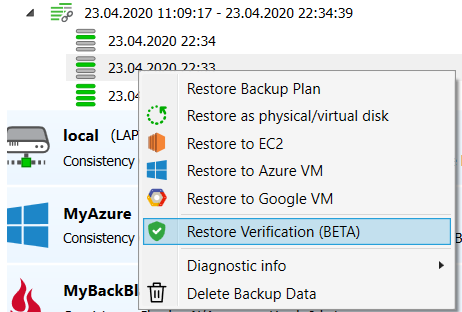
This creates and runs a test restore plan that starts a Hyper-V VM using a necessary part of the backed up data downloaded from backup storage. To check that the test virtual machine is running, see its state in the preview:
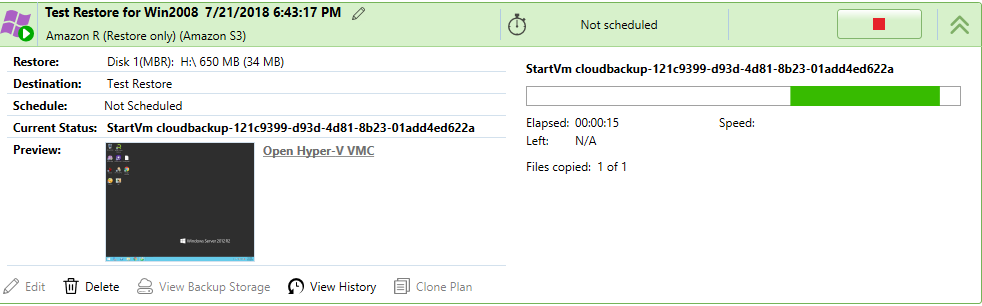
- Optionally, to log on to VM, click the Open Hyper-V VMC link.
Enable Restore Verification in Backup Plan
You can apply Restore Verification on a regular basis by including it in a backup plan.
To Enable Restore Verification
- Edit an image-based backup plan you intend to apply this feature.
- Follow the Backup Wizard steps to the Consistency Check and Restore Verification subsection of the Image-Based Backup Plan chapter.
- Select the restore verification run option:
- Do not Run Restore Verification. Select this option to run restore verification manually
- Run for Full only. Select this option to run restore verification for full backups only. You can manage a schedule for full and incremental backups on the Schedule step of the Backup Wizard
- Run for Incremental only. Select this option to run restore verification for incremental backups only. You can manage a schedule for full and incremental backups on the Schedule step of the Backup Wizard
- Run for Full and Incremental. Select this option to run restore verification for both backup types.
- Click Advanced Settings to specify Hyper-V VM settings:
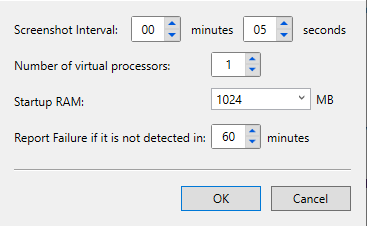
- In the Screenshot Interval, specify the frequency of making a screenshot of a Hyper-V VM to check its state by sight
- In the Number of virtual processors, specify the number of virtual CPUs for Hyper-V VM
- In the Startup RAM, specify the part RAM allocated for restore verification VM
- In Report Failure if it is not detected in: field, specify the period after which Restore Verification will be terminated with an error
Click OK.
Follow other Backup Wizard steps to save the configuration of this backup plan.
In some cases, if a volume with a temporary folder is full, a restore verification can terminate with the following error: Cannot complete Restore Verification. Not enough space in the temporary folder: c:\temp
Once this error occurs, clean up the temporary folder, or change its location to the other volume with more free space. To do this, proceed as follows:
- In the Tools menu, select Options.
- Switch to the Memory Options tab.
- In the Temporary folder field, specify the temporary folder location.
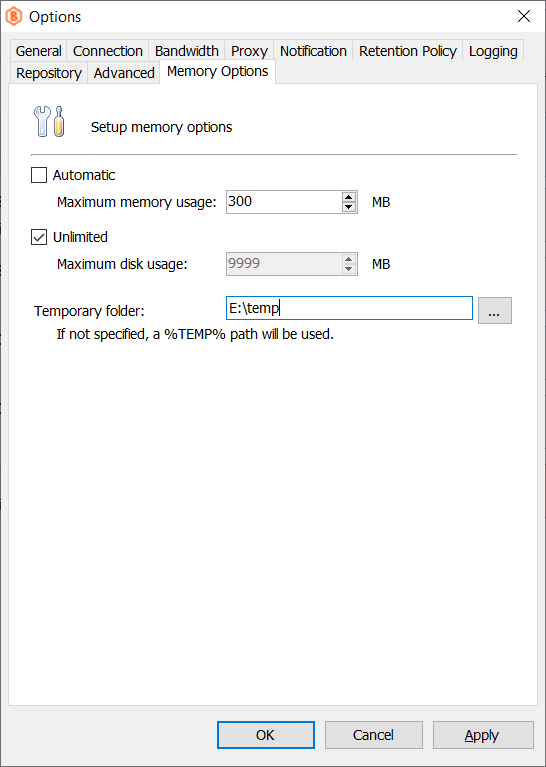
- Click OK or Apply.
To learn more about Hyper-V, refer to the Virtualization article at docs.microsoft.com.
Restore Verification in Long-Term Storage
In case your storage destination is a long-term one (this can be S3 Glacier, S3 Deep Archive, or Azure Archive storage classes), Restore Verification is disabled.
Since Restore Verification requires downloading parts of data from a cloud, in a case with long-term storage it will take up significant time, up to several hours. Additionally, retrieval costs are subject to extra charges on backup data downloads from the cloud.